Requirements engineering is an important phase in a software engineering lifecycle. There are different approaches on how to elicit requirements. The term of artefact-oriented requirements engineering has been coined recently. Artefact-oriented requirements engineering focuses only on the outcome of the engineering phase, the so-called artefacts. The process leading to the creation of the artefacts is not predefined and can be chosen as required. Up to date there exist a generic meta model for artefact-orientation as well as a couple of instances. For this thesis AMDiRE (Artefact Model for Domain-independent Requirements Engineering) and the BISA model, a model for Business Information Systems' Analysis, are of particular interest.
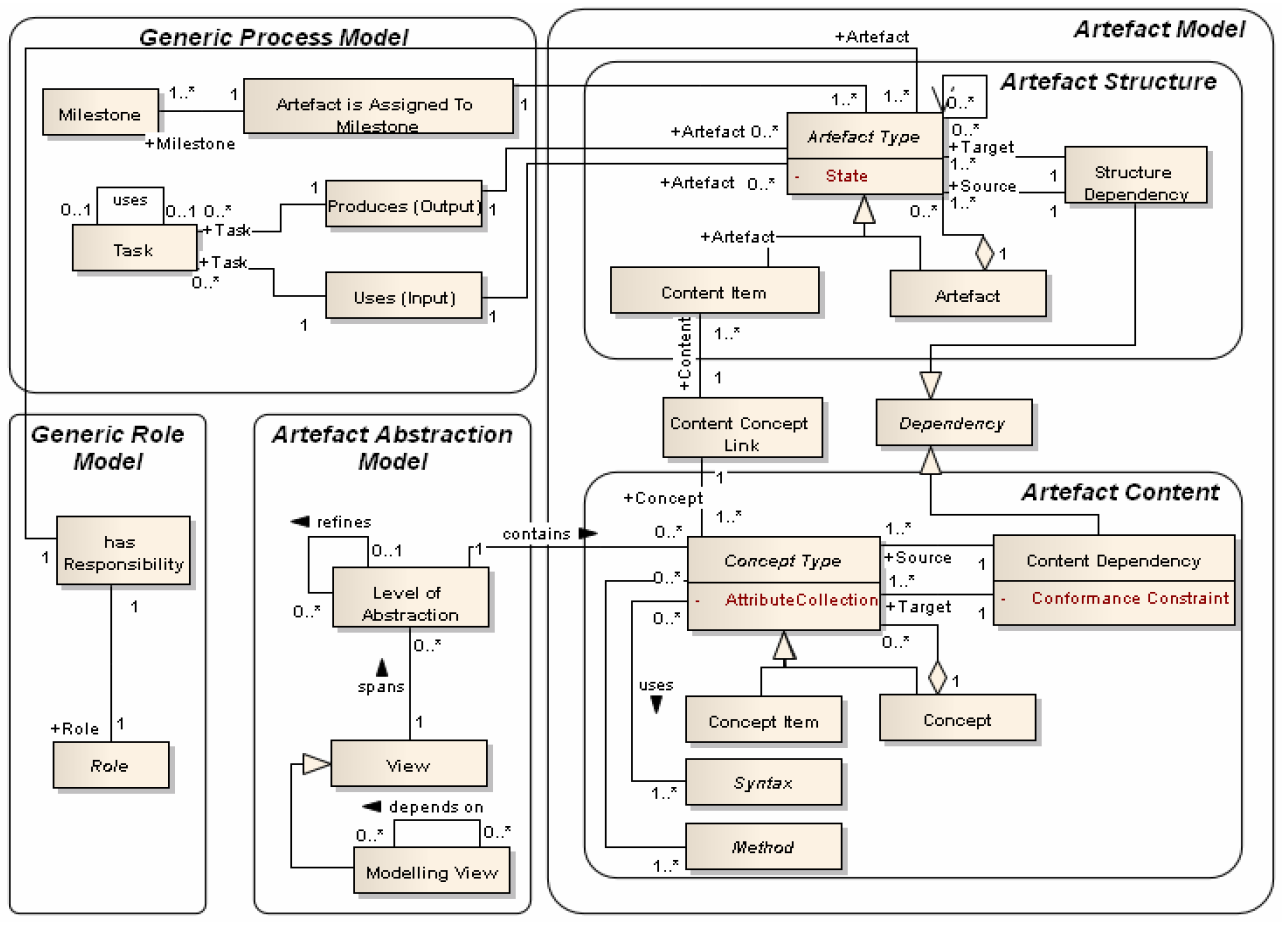
The meta model for artefact-orientation. (Source: Méndez Fernández et al. - A Meta Model for Artefact-Orientation: Fundamentals and Lessons Learned in Requirements Engineering)
The implicit process involved in artefact-oriented requirements engineering is knowledge-intensive. Therefore, doing artefact-oriented requirements engineering is considered knowledge work. Successfully fulfilling knowledge work tasks depends significantly on the knowledge of the worker. More precisely, instead of doing repeatable routine work, the knowledge worker has to decide how to solve a problem and therefore has to adapt to changing circumstances.
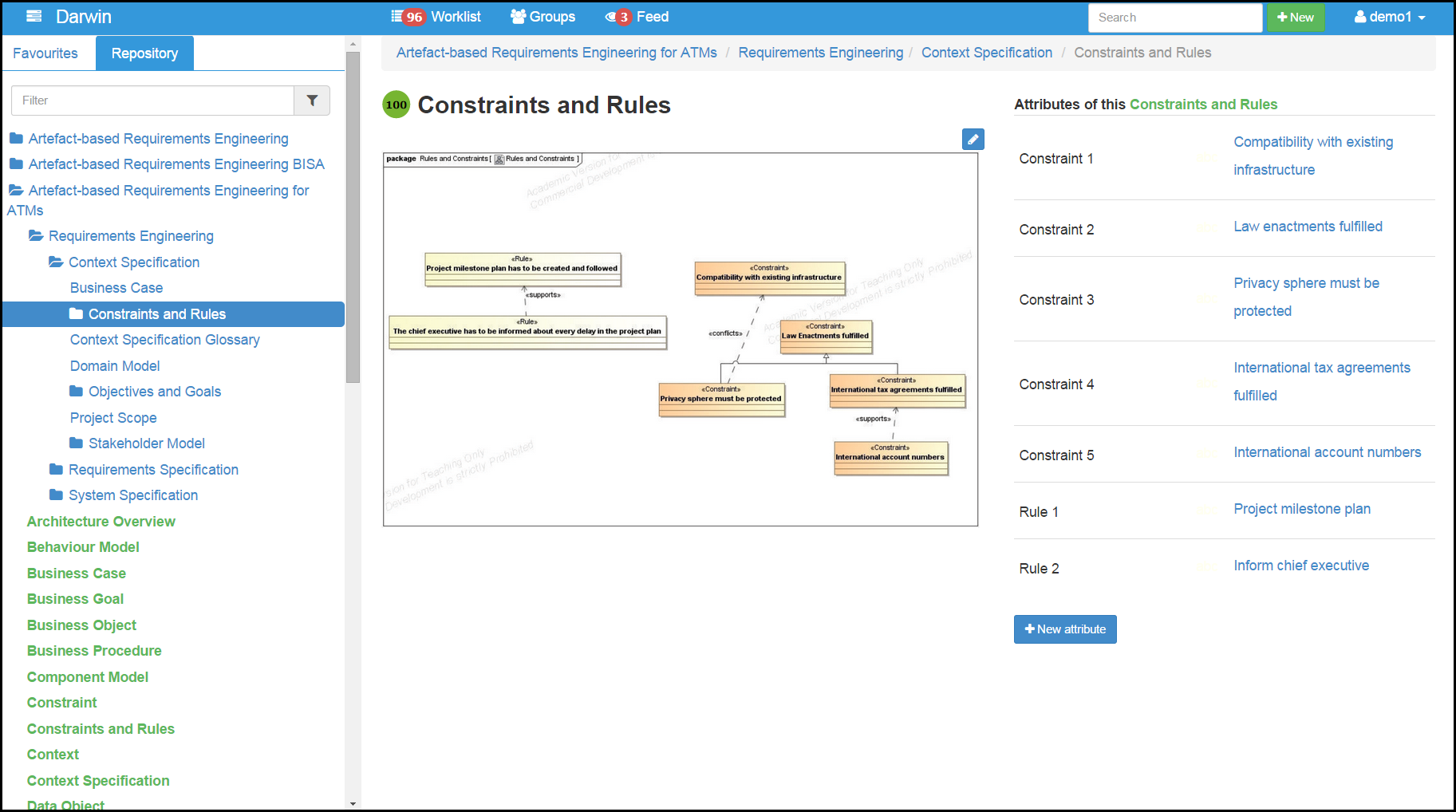
Screenshot of a demo page in Darwin which is based on the artefacts of AMDiRE (Artefact content taken from: Besner - Evaluation of an Artefact-based Requirements Engineering Approach).
This master's thesis looks into ways of supporting artefact-oriented requirements engineering by a software tool for knowledge-intensive processes. Furthermore, an evaluation of the developed concepts is provided. Currently tools which support AMDiRE or the BISA model are not available. As these models basically just describe the artefacts, the requirements of the corresponding knowledge-intensive processes have to be determined first. Therefore, this thesis examines the process characteristics of the process in the meta model as well as in AMDiRE and in the BISA model. Furthermore, a concrete way of supporting artefact-oriented requirements engineering by a software tool is depicted. Therefore, an evaluation is presented based on three demo implementations. The evaluation relies on the Darwin web application which has been especially created for application areas containing knowledge-intensive processes.
Literature